Article 1, Section 9, Clause 8
[Volume 3, Page 388]
Document 13
Thomas Jefferson to John Adams
28 Oct. 1813 Cappon 2:389--92
Cappon 2:389--92
It is probable that our difference of opinion may in some
measure be produced by a difference of character in those
among whom we live. From what I have seen of Massachusets
and Connecticut myself, and still more from what I
have heard, and the character given of the former by
yourself, who know them so much better, there seems to
be in those two states a traditionary reverence for certain
families, which has rendered the offices of the government
nearly hereditary in those families. I presume that from
an early period of your history, members of these families
happening to possess virtue and talents, have honestly exercised
them for the good of the people, and by their services
have endeared their names to them.
In coupling Connecticut with you, I mean it politically
only, not morally. For having made the Bible the Common
law of their land they seem to have modelled their morality
on the story of Jacob and Laban. But altho' this hereditary
succession to office with you may in some degree be
founded in real family merit, yet in a much higher degree
it has proceeded from your strict alliance of church and
state. These families are canonised in the eyes of the people
on the common principle 'you tickle me, and I will
tickle you.' In Virginia we have nothing of this. Our
clergy, before the revolution, having been secured against
rivalship by fixed salaries, did not give themselves the trouble
of acquiring influence over the people. Of wealth, there
were great accumulations in particular families, handed
down from generation to generation under the English law
of entails. But the only object of ambition for the wealthy was
a seat in the king's council. All their court then was paid to
the crown and it's creatures; and they Philipised in all collisions
between the king and people. Hence they were unpopular;
and that unpopularity continues attached to their
names. A Randolph, a Carter, or a Burwell must have great
personal superiority over a common competitor to be elected
by the people, even at this day.
At the first session of our legislature after the Declaration
of Independance, we passed a law abolishing entails.
And this was followed by one abolishing the privilege of
Primogeniture, and dividing the lands of intestates equally
among all their children, or other representatives. These
laws, drawn by myself, laid the axe to the root of Pseudoaristocracy.
And had another which I prepared been
adopted by the legislature, our work would have been
compleat. It was a Bill for the more general diffusion of
learning. This proposed to divide every county into wards [Volume 3, Page 389]
of 5. or 6. miles square, like your townships; to establish
in each ward a free school for reading, writing and common
arithmetic; to provide for the annual selection of the
best subjects from these schools who might receive at the
public expence a higher degree of education at a district
school; and from these district schools to select a certain
number of the most promising subjects to be compleated
at an University, where all the useful sciences should be
taught. Worth and genius would thus have been sought
out from every condition of life, and compleatly prepared
by education for defeating the competition of wealth and
birth for public trusts.
My proposition had for a further object to impart to
these wards those portions of self-government for which
they are best qualitifed, by confiding to them the care of
their poor, their roads, police, elections, the nomination of
jurors, administration of justice in small cases, elementary
exercises of militia, in short, to have made them little republics,
with a Warden at the head of each, for all those
concerns which, being under their eye, they would better
manage than the larger republics of the county or state. A
general call of ward-meetings by their Wardens on the
same day thro' the state would at any time produce the
genuine sense of the people on any required point, and
would enable the state to act in mass, as your people have
so often done, and with so much effect, by their town
meetings. The law for religious freedom, which made a
part of this system, having put down the aristocracy of the
clergy, and restored to the citizen the freedom of the
mind, and those of entails and descents nurturing an
equality of condition among them, this on Education
would have raised the mass of the people to the high
ground of moral respectability necessary to their own
safety, and to orderly government; and would have compleated
the great object of qualifying them to select the
veritable aristoi, for the trusts of government, to the exclusion
of the Pseudalists: and the same Theognis who has
furnished the epigraphs of your two letters assures us that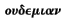
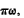
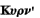
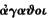
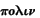
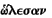
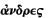 ["Curnis,
good men have never harmed any city"]. Altho' this law
has not yet been acted on but in a small and inefficient
degree, it is still considered as before the legislature, with
other bills of the revised code, not yet taken up, and I have
great hope that some patriotic spirit will, at a favorable
moment, call it up, and make it the key-stone of the arch
of our government.
["Curnis,
good men have never harmed any city"]. Altho' this law
has not yet been acted on but in a small and inefficient
degree, it is still considered as before the legislature, with
other bills of the revised code, not yet taken up, and I have
great hope that some patriotic spirit will, at a favorable
moment, call it up, and make it the key-stone of the arch
of our government.
With respect to Aristocracy, we should further consider
that, before the establishment of the American states,
nothing was known to History but the Man of the old
world, crouded within limits either small or overcharged,
and steeped in the vices which that situation generates. A
government adapted to such men would be one thing; but
a very different one that for the Man of these states. Here
every one may have land to labor for himself if he chuses;
or, preferring the exercise of any other industry, may exact
for it such compensation as not only to afford a comfortable
subsistence, but wherewith to provide for a cessation
from labor in old age. Every one, by his property, or
by his satisfactory situation, is interested in the support of
law and order. And such men may safely and advantageously
reserve to themselves a wholsome controul over
their public affairs, and a degree of freedom, which in the
hands of the Canaille of the cities of Europe, would be
instantly perverted to the demolition and destruction of
every thing public and private. The history of the last 25.
years of France, and of the last 40. years in America, nay
of it's last 200. years, proves the truth of both parts of this
observation.
But even in Europe a change has sensibly taken place in
the mind of Man. Science had liberated the ideas of those
who read and reflect, and the American example had kindled
feelings of right in the people. An insurrection has
consequently begun, of science, talents and courage
against rank and birth, which have fallen into contempt. It
has failed in it's first effort, because the mobs of the cities,
the instrument used for it's accomplishment, debased by
ignorance, poverty and vice, could not be restrained to rational
action. But the world will recover from the panic of
this first catastrophe. Science is progressive, and talents
and enterprize on the alert. Resort may be had to the people
of the country, a more governable power from their
principles and subordination; and rank, and birth, and
tinsel-aristocracy will finally shrink into insignificance,
even there. This however we have no right to meddle with.
It suffices for us, if the moral and physical condition of
our own citizens qualifies them to select the able and good
for the direction of their government, with a recurrence
of elections at such short periods as will enable them to
displace an unfaithful servant before the mischief he meditates
may be irremediable.
I have thus stated my opinion on a point on which we
differ, not with a view to controversy, for we are both too
old to change opinions which are the result of a long life
of inquiry and reflection; but on the suggestion of a former
letter of yours, that we ought not to die before we
have explained ourselves to each other. . . .
Of the pamphlet on aristocracy which has been sent to
you, or who may be it's author, I have heard nothing but
thro' your letter. If the person you suspect it may be
known from the quaint, mystical and hyperbolical ideas,
involved in affected, new-fangled and pedantic terms,
which stamp his writings. Whatever it be, I hope your
quiet is not to be affected at this day by the rudeness of
intemperance of scribblers; but that you may continue in
tranquility to live and to rejoice in the prosperity of our
country until it shall be your own wish to take your seat
among the Aristoi who have gone before you. Ever and
affectionately yours.
The Founders' Constitution
Volume 3, Article 1, Section 9, Clause 8, Document 13
http://press-pubs.uchicago.edu/founders/documents/a1_9_8s13.html
The University of Chicago Press
The Adams-Jefferson Letters: The Complete Correspondence between Thomas Jefferson and Abigail and John Adams. Edited by Lester J. Cappon. 2 vols. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press for the Institute of Early American History and Culture, Williamsburg, Virginia, 1959.
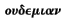
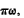
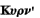
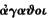
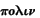
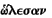
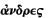 ["Curnis,
good men have never harmed any city"]. Altho' this law
has not yet been acted on but in a small and inefficient
degree, it is still considered as before the legislature, with
other bills of the revised code, not yet taken up, and I have
great hope that some patriotic spirit will, at a favorable
moment, call it up, and make it the key-stone of the arch
of our government.
["Curnis,
good men have never harmed any city"]. Altho' this law
has not yet been acted on but in a small and inefficient
degree, it is still considered as before the legislature, with
other bills of the revised code, not yet taken up, and I have
great hope that some patriotic spirit will, at a favorable
moment, call it up, and make it the key-stone of the arch
of our government.